Math 3118, section 4
Spring 2002
Review 2 solutions
Answers are shown in magenta.
1. Let f(x) = x3 +
3x2 - 3, where x is a real variable.
- Fill in the following table of values:
|
x |
-4 |
-3 |
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
f (x) |
-19 |
-3 |
1 |
-1 |
-3 |
1 |
17 |
- On which of the following intervals does the Intermediate Value Theorem say that f(x) has a real zero?
- Between -4 and -3 No sign change, so IVT does not predict a zero.
- Between -3 and -2 Changes sign, so there is a zero.
- Between -2 and -1 Changes sign, so there is a zero.
- Between -1 and 0 No sign change, so IVT does not predict a zero.
- Between 0 and 1 Changes sign, so there is a zero.
- Between 1 and 2 No sign change, so IVT does not predict a zero.
- (Optional) if you have a graphing calculator, plot the graph of
f.
2.
Compute the following complex numbers:
- (3 + 4i)·(4 + i)
=12 + 3i+ 16i+ 4i2
= 12 + 3i+ 16i- 4 = 8 + 19i
- (3 + 2i)·(2 - i)
= 6 - 3i+ 4i- 2i2
= 6 - 3i+ 4i+ 2 = 8 + i
- the complex conjugate of 4 + 3i
is 4 - 3i
- the complex conjugate of - 6i
is 6i
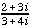 =
=
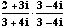 =
=
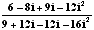 =
=
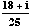
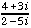 =
=
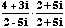 =
=
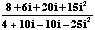 =
=
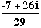
3. Use the method of exercise 10.2.9 to approximate 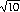 . Start with a=3, and stop when the difference between the upper and lower estimates is less than .000001.
. Start with a=3, and stop when the difference between the upper and lower estimates is less than .000001.
- First stage
- Start with a = 3
- Divide into 10: b = 10 ÷ a =
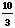 =
= 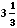
- Average previous two: c =
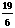 =
= 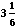
- Square to check: c2 =
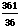 =
= 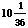
- Second stage:
- a
= 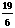 = previous c
= previous c
- Divide into 10: b = 10 ÷ a =
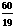 =
= 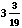
- Average previous two: c =
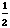 ·
·
(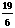 +
+ 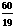 ) =
) = 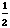 ·
·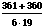 =
= 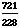 = 3.162280702
= 3.162280702
- Square to check: c2 =
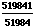 =
= 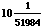 = 10.00001924.
= 10.00001924.
Third stage:
- a
= 3.162280702 = previous c
- Divide into 10: b = 10 ÷ a = 3.162274619
- Average previous two: c = 3.16227766
- Square to check: c2 = 10 + e, where e is approximately equal to 10-11.
So, the answer is 3.16227766.
4.
Find all of the zeros of the polynomial:
x3 + 2x2 - x - 2
- The rational numbers which
could be zeros of this polynomial are the (positive and
negative) factors of 2, thus: 1, -1, 2, -2.
- We substitute these values into the polynomial, obtaining 0 when we
substitute 1, -1, and -2, but obtaining 8 + 8 - 2 - 2 = 12
when we substitute 2.
- So, 1, -1, and -2 are the roots.
Factor this polynomial as a product of 3 linear factors.
- We work with one or our known roots, for instance -2.
- So, we expect that x-(-2) = x+2 will be a factor.
- We use division of polynomials to get the factorization:
x3 + 2x2 - x - 2 = (x + 2)(x2 - 1).
- We can factor x2 - 1 as:
x2 - 1 = (x - 1)(x + 1).
- So, our original polynomial factors as:
x3 + 2x2 - x - 2 = (x + 2)(x - 1)(x + 1).
5.
Find a rational zero of each polynomial, and then factor the polynomial as a product of a linear factor and a quadratic factor.
- 2x3 - 7x2 + 5x - 1
- The rational numbers which
conceiveably could be zeros of this polynomial are the (positive and
negative) rational numbers [quotients of integers] whose numerators are
factors of 1 and whose denominators are factors of 2, thus:
1, -1, 1/2, -1/2.
- Substituting 1 and -1 gives odd numbers (thus not zero).
Substituting 1/2 gives 0.
Substituting -1/2 gives -11/2 (also not zero).
So, 1/2 is the only rational zero.
- Using division of polynomials, we find the following factorization:
2x3 - 7x2 + 5x - 1 =
(x - 1/2)(2x2 - 6x + 2)
- x3 - 7x2 +5x + 1
- The rational numbers which
conceiveably could be zeros of this polynomial are 1 and -1.
Substituting 1 gives 0.
Substituting -1 gives -14 (certainly not zero).
So, 1 is the only rational zero.
- Using division of polynomials, we find the following factorization:
x3 - 7x2 + 5x + 1 = (x - 1)(x2 - 6x - 1)
6.
For each polynomial in the preceding problem, find all of its zeros (whether rational, real, or complex).
Suggestion: Use the quadratic formula to find the zeros of the quadratic factor.
- Solution:
-
- 2x3 - 7x2 + 5x - 1 = (x - 1/2)(2x2 - 6x + 2)
- Applying the quadratic formula to 2x2 - 6x + 2,
we find the roots
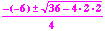 ;
;
thus 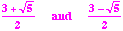 .
.
- So, the zeros of the third degree polynomial are
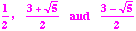
- x3 - 7x2 +5x - 1 = (x - 1)(x2 - 6x - 1)
- Applying the quadratic formula to x2 - 6x -1, we find the roots
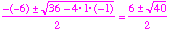 ,
,
thus 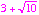 and
and 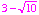 .
.
- So, the zeros of the third degree polynomial are 1,
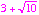 , and
, and 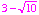 .
.
7.
- Explain why
 and
and
 are algebraic.
are algebraic.
Because they are roots of the polynomials
x2 - 2 and x2 - 5 respectively.
- Write (
 +
+
 )2 as
A + B
)2 as
A + B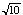 , where A
and B are rational numbers.
, where A
and B are rational numbers.
Solution:
( +
+  )2 = 7 + 2
)2 = 7 + 2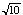
- Write (
 +
+
 )4 as
A + B
)4 as
A + B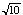 , where A
and B are rational numbers .
, where A
and B are rational numbers .
Solution:
( +
+  )4 = (7+ 2
)4 = (7+ 2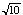 )2 = 89 + 28
)2 = 89 + 28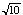 .
.
- Find a rational number S such that
(
 +
+  )4 + S(
)4 + S(
 )
is a rational number.
)
is a rational number.
Substituting from
parts b and c, we have:
( +
+  )4 + S(
)4 + S( +
+  )2 =
(89 + 28
)2 =
(89 + 28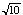 ) + S(7 + 2
) + S(7 + 2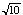 ).
).
We can re-arrange this as:
( +
+  )4 + S(
)4 + S( +
+  )2 =
(89 + 7S) + (28 + 2S)
)2 =
(89 + 7S) + (28 + 2S)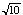 .
.
To solve the problem, we must choose S so that
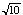 disappears from
the answer.
disappears from
the answer.
To do this, we need to have
28 + 2S = 0. Therefore
S = -14.
- Find rational numbers S and T such that
(
 +
+  )4 + S(
)4 + S( +
+  )2 + T = 0.
)2 + T = 0.
Taking S = -14 and
substituting into the second long equation in part d, we have:
( +
+  )4 - 14(
)4 - 14( +
+  )2 =
(89 + 7(-14)) + (28 + 2(-14))
)2 =
(89 + 7(-14)) + (28 + 2(-14))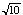 ,
or simply:
,
or simply:
( +
+  )4 - 14(
)4 - 14( +
+  )2 = -9.
(Note that 89 + 7(-14) = 89 - 98 = -9.)
)2 = -9.
(Note that 89 + 7(-14) = 89 - 98 = -9.)
Adding 9 to both sides of the equation, we get:
( +
+  )4 - 14(
)4 - 14( +
+  )2 + 9 = 0.
)2 + 9 = 0.
In other words, T = 9.
(This shows that  +
+  is also algebraic, since we
now have the equation:
is also algebraic, since we
now have the equation:
( +
+  )4 - 14(
)4 - 14( +
+  )2 + 9 = 0. )
)2 + 9 = 0. )
As an alternative, we can combine parts d and e,
thus solving simultaneously for S and
T,
as follows:
Substituting from
parts b and c, the equation
( +
+  )4 + S(
)4 + S( +
+  )2 + T = 0
)2 + T = 0
is the same as
(89 + 28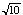 ) + S(7 + 2
) + S(7 + 2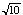 ) + T = 0.
) + T = 0.
We can re-arrange this as:
(89 + 7S + T) + (28 + 2S)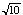 = 0.
= 0.
So, we have these equations:
89 + 7S + T = 0
28 + 2S = 0.
From the second equation we see that S = -14. Substituting into the
first equation, we have:
89 - 98 + T = 0, or T = 9.
(Once again, we see that  +
+  is also algebraic, since we
have obtained the equation:
is also algebraic, since we
have obtained the equation:
( +
+  )4 - 14(
)4 - 14( +
+  )2 + 9 = 0. )
)2 + 9 = 0. )
8.
- (Exercise 10.1.13) No, the irrational numbers do not form a subfield of the real numbers.
Since the sum of two elements of a subfield is supposed to again be an element of the subfield,
it's sufficient to note that the sum of two irrational numbers need not be irrational, as shown
in Exercise 10.1.11. If we want further corroboration of this answer, we can also note that
the product of two irrational numbers need not be irrational, as shown in Exercise 10.1.12.
- (Exercise 10.2.1) To six decimal places,
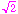 is approximately equal to 1.414214… .
is approximately equal to 1.414214… .
(The dots just indicate that the decimal expansion of 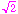 doesn't end at that stage.)
doesn't end at that stage.)
Therefore, 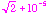 is approximately equal to 1.414224…. So, one choice of a rational number
is approximately equal to 1.414224…. So, one choice of a rational number
(or terminating decimal) in this range is 1.414220 = 1.41422.
- (Exercise 10.4.11)
(1 + i)2 = (1 + i)·(1 + i) = 1 + 2i + i2 = 2i. (FOIL; then recall that i2 = -1).
Therefore:
(1 + i)4 = (1 + i) 2·(1 + i) 2 = 2i·2i = 4 i2 = -4,
and finally:
(1 + i)5 = (1 + i) 4·(1 + i) = -4·(1 + i) = -4 - 4i.
Back to:
![]() . Start with a=3, and stop when the difference between the upper and lower estimates is less than .000001.
. Start with a=3, and stop when the difference between the upper and lower estimates is less than .000001.
 )2 =
(89 + 7(-14)) + (28 + 2(-14))
)2 =
(89 + 7(-14)) + (28 + 2(-14)) )2 = -9.
(Note that 89 + 7(-14) = 89 - 98 = -9.)
)2 = -9.
(Note that 89 + 7(-14) = 89 - 98 = -9.) )2 + 9 = 0.
)2 + 9 = 0.